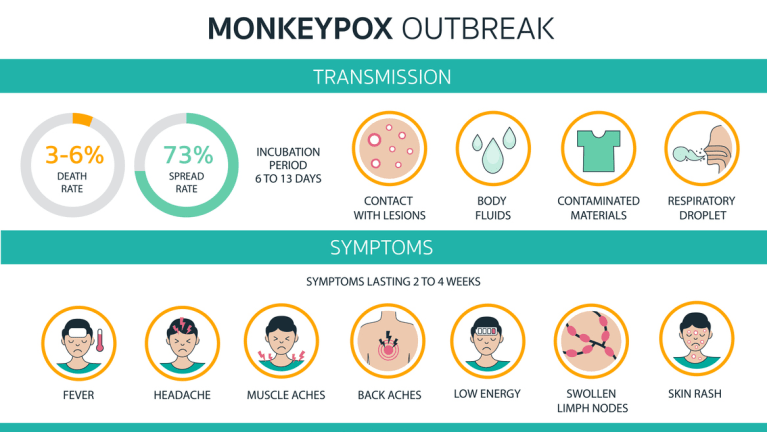
Monkeypox is a rare and infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus. It is similar to smallpox, but generally less severe. Outbreaks of monkeypox have been reported in several African countries, including the Democratic Republic of Congo, Nigeria, and Uganda.
The symptoms of monkeypox typically appear within 2 to 4 weeks after exposure to the virus and may include fever, headache, muscle aches, backache, swollen lymph nodes, chills, fatigue, and a rash that progresses from red bumps to blister-like lesions. The lesions may be filled with fluid and may crust over and form scabs. In some cases, the lesions may affect the eyes, mouth, or genital area, and may cause painful swallowing or difficulty breathing.
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but symptoms can be managed with supportive care, such as pain relief and hydration. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
There is currently no licensed vaccine for monkeypox in the United States, but the smallpox vaccine may provide some protection against the virus. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the use of the smallpox vaccine in outbreak situations, but its use is limited due to the potential for side effects and the fact that it is no longer routinely used.